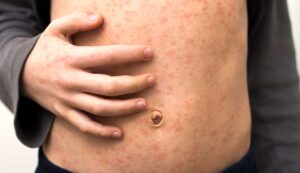
An acute infectious viral disease characterized by ‘Kalpak’s spots’, high fever, nasal catarrh, cough and blotchy rash.
 |
| source cleveland clinic |
CLINICAL FEATURES
Ø Prodromal stage: Duration: 1-4 days.
Symptoms
- Onset:
- Sudden.
- High fever
- Coryza
- Sneezing.
- Lachrymation.
- Photophobia.
- Hoarseness.
- Hacking cough.
ETIOLOGY
Distribution: Worldwide.
Season: Common during winter.
Causative organism: Measles virus.
Source: Human respiratory discharges.
Predisposing causes: Poor sanitation, poor nutrition and overcrowding.
Transmission: By direct contact, droplet infection.
Incubation period: 8-14 days.
Age: 3-5 years.
Signs
- Temperature: 40 °C-41 °C.
- Pulse: relative bradycardia.
- Face: congested.
- Eyes: congested.
- On 2nd day:
Koplik’s spots become apparent (Koplik’s spots are tiny whitish spots At buccal mucous membrane opposite upper second molar).
On 3rd day:
Temperature: normal.
Exanthematous stage
Duration: 4-7 days.
Symptoms
- Fever rises again on 4th day.
- Headache.
- Retro – Orbital pain
- Lachrymation.
- Photophobia.
- Hacking cough.
- Rash appear on 4th day.
Signs:
- Temperature: 40 °C-41 °C.
- Pulse: fast
- Face: puffy.
- Eyes: congested.
- Rash: Pink, maculo-papular. Appears first on forehead and spreads to whole body within few hours. Blanches on pressure.
Convalescent stage
Duration: 7 days.
Symptoms:
- Fever subsides within 1-2 days.
- Rash fades from above downwards.
- Brown stained desquamation.
- Desquamation subsides within 1-2 weeks.
COMPLICATIONS
- Immediate
- Otitis media
- Bronchitis
- Pneumonia
- Late
- Bronchiectasis
Sub acute sclerosing pan encephalitis (after 5- 7 years).
(A rare, chronic progressive and fatal neurological complication of measles. It is characterised by insidious onset with intellectual deterioration, apathy and clumsiness, followed by myoclonic jerks, rigidity and dementia in children and adolescents. EEG. is characteristic; shows bursts of triphasic slow waves.)
PROGNOSIS
Good.
GENERAL MANAGEMENT
Bed rest till fever and rash disappear.
Activities like reading, T.V. watching must be restricted till conjunctivitis subsides.
Hydrotherapy during high fever, plenty of fluids should be given to the patient.
Avoid very cold things.
PROPHYLACTIC MEASURES
Immediate
Isolation.
Children should be sent to school 7 days after defervescence.
Prevention of close contacts.
Hygienic disposal of infected secretions.
Long term
Immunization (as per national health programme).
Improve general health.
MEDICAL TREATMENT
Prodromal state
Aconite: First stage of measles, sudden high fever. History of exposure to cold air. Child is restless, wants to be carried. Bright red rough rash. Redness of the eyes. Dry, barking, croupy cough, pulse rapid. Very thirsty for cold drinks. Chilly.
Belladonna: Cold, fever high.
Euphrasia: Early stage of measles. Eyes are sensitive to light. Constant hot irritating lachrymation. Bland nasal discharge. Measles rash. Pain in the forehead. Worse; sunlight, indoor, warm room. Better open air, blinking, wiping the eyes.
Ferrum phosphoricum: Fever with congestion of chest.
Gelsemium: Dizzy, dull, drowsy. Bodyache. Fever. Irritating, watery nasal discharge.
Malignant measles
Arsenicum album: Malignant or black or haemorrhagic measles. Sinking of strength. Diarrhoea, delirium, restlessness. Debility. Petechiae. Offensive and exhausting stools.