INTRODUCTION Left ventricular (LV) dysfunction
Left ventricular (LV) dysfunction is a condition in which the heart’s left ventricle doesn’t pump blood as effectively as it should. It can be a silent condition that’s potentially deadly.
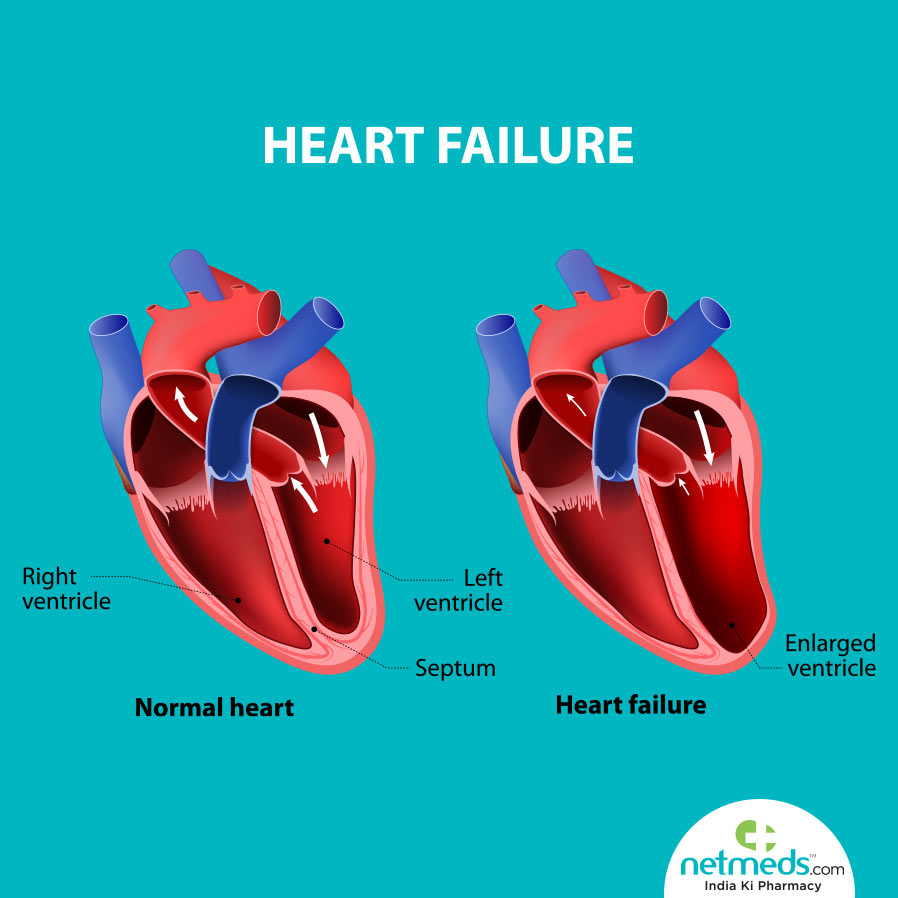
Types of LV dysfunction
- Systolic dysfunction
The ventricle has trouble contracting firmly, which reduces the amount of blood pumped out with each beat.
- Diastolic dysfunction
The ventricle doesn’t relax and fill properly during the diastolic portion of the cardiac cycle.
Symptoms Left ventricular (LV) dysfunction
- Fatigue and pain
- Depression and anxiety
- Reduced stamina
- Wheezing and coughing
- Increased heartbeat
- Loss of appetite
- Sudden weight gain
Cause Left ventricular (LV) dysfunction
Coronary artery narrowing or ischemic heart disease, Cardiomyopathy, Hypertension, Valve disease, and Myocarditis.
Treatment Left ventricular (LV) dysfunction
- Medications, such as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking and alcohol
Risk factors Left ventricular (LV) dysfunction
LV dysfunction is associated with cardiovascular mortality and ischemic stroke. It’s also associated with increased age, lower educational attainment, and higher prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and coronary heart disease.